Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin found in animal products and supplements.It is responsible for crucial processes in our bodies like DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) synthesis, red blood cell production and nerve health.
Its importance however, goes beyond these metabolic processes, with recent studies showing its potential benefits in skin diseases, especially dermatitis. Dermatitis refers to a group of inflammatory skin diseases that are characterised by redness, itching and irritation of the skin, which can severely affect the quality of life of the individual.
As a barrier, the skin protects the body against harmful environmental agents, therefore maintaining its integrity is critical to health. Vitamin B12 is thought to help with skin health by way of its anti-inflammatory effects and its role in cellular regeneration.
Types and signs
Dermatitis is a term used to cover a wide range of inflammatory skin conditions that feature redness, swelling and itching. Each of these conditions have their own specific triggers and symptoms, although they share certain underlying mechanisms such as inflammation and impaired function of the skin barrier. Here are some common types of dermatitis:
> Atopic dermatitis
A chronic condition that frequently begins in childhood, it is linked to a family history of allergies or asthma. Atopic dermatitis can cause dry, itchy skin, and often results in a sizeable burden of symptomatology, which can have a negative impact on quality of life.
> Contact dermatitis
This is when the skin reacts to the touch of allergens or irritants. There are two major types of contact dermatitis: allergic, which is a reaction from the immune system to a substance it does not like, and irritant, which leads to direct damage to the skin.
> Seborrhoeic dermatitis
This condition affects areas with a lot of oil glands, like the scalp and face, where it appears as red, scaly patches. It’s often associated with factors like stress, hormonal fluctuations and overgrowth of fungi.
> Nummular dermatitis
This form of eczema presents as round, coin-shaped plaques of inflamed skin. It is commonly triggered by dry skin. Dermatitis varies in symptoms depending on its type and severity. However, common signs include:
- Redness and inflammation
- An itching or burning feeling
- Dry, scaly or crusted patches
- And in some cases, blisters or weeping sores.
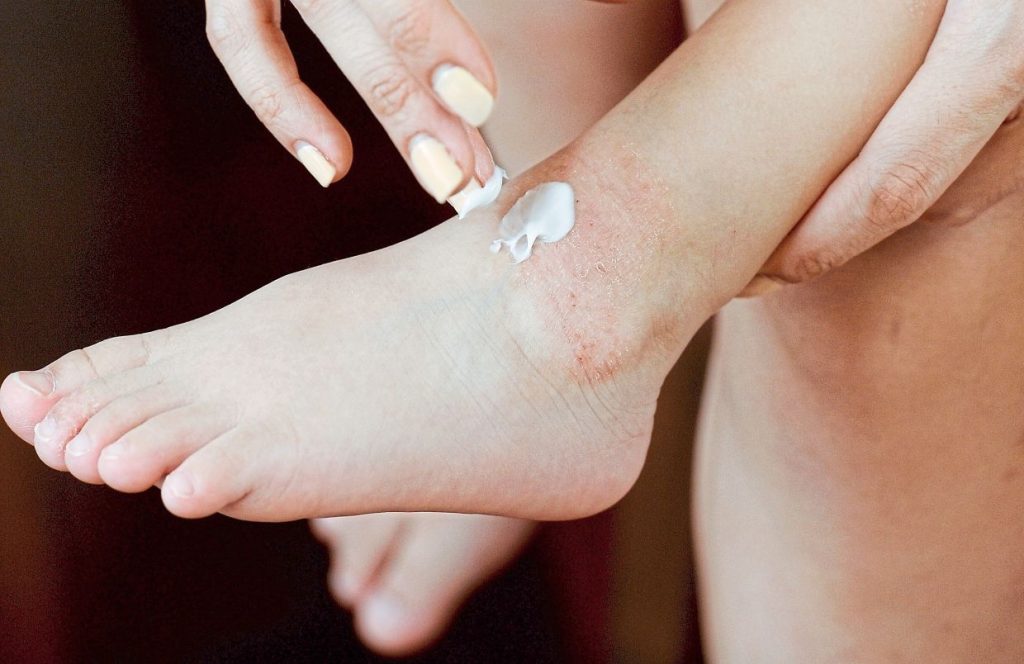
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of dermatitis is usually made by careful clinical assessment, including a complete medical history and physical examination. In certain cases, patch tests or skin biopsies are done to detect specific allergens or to exclude other skin diseases.
Treatment for dermatitis is often focused on relieving the symptoms and restoring the barrier for the skin. Common approaches include:
- Topical corticosteroidsThese are often prescribed to decrease inflammation and itching.Long-term use though, can cause skin-thinning and other problems.
- MoisturisersEmollients should be applied frequently to keep the skin hydrated and support the skin barrier.
- AntihistaminesThese may be suggested for patients with severe pruritus (itchiness) to manage the itching and allow better sleep quality.
- ImmunomodulatorsNon-steroidal topical agents like calcineurin inhibitors may be used as alternatives to steroids for sensitive areas.
A promising alternative
Recent clinical studies have started showing the benefits of using vitamin B12 cream to help manage dermatitis. Vitamin B12 has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, which may help reduce the inflammatory processes typical of dermatitis.
In one study, patients applying vitamin B12 cream reported experiencing significant reductions in redness and itchiness, compared to those using a placebo. This vitamin has also been shown to improve skin barrier function in individuals with dermatitis.
By helping to restore the integrity of the skin barrier, it helps protect us from irritants and allergens that could lead to flare-ups, as well as maintaining the health of the skin. Vitamin B12 cream compounding is a process that creates customised topical formulations with vitamin B12 integrated into them, helping to match the needs of the individual patient.
This not only boosts the healing properties of vitamin B12, but also enables the addition of other helpful ingredients that could help promote skin health even more. Compounding focuses on particular customer needs that mass manufactured products do not meet.
Such formulations can be tailored to enhance effectiveness and minimise unwanted effects. These customised preparations can be obtained from compounding pharmacies.
While dermatologists can start to explore the potential use of vitamin B12 cream in helping their patients to manage dermatitis, it is important to note that further research is still needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying the actions of vitamin B12 when it comes to this chronic skin condition.
More clinical studies are also needed to clarify the ideal formulation, dose and method of delivery for vitamin B12 cream in dermatitis. With more scientific evidence, vitamin B12 could prove to be a safe alternative to topical steroids and an adjunctive therapy in the management of dermatitis.
By Datuk Dr Nor Ashikin Mokhtar
Published in Star Newspaper, 21 Apr 2025